Technology guide
Why choose Red Hat for continuous IT security
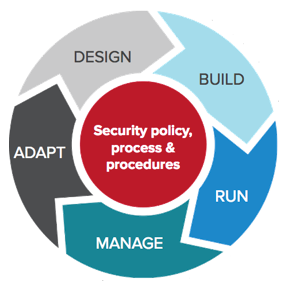
IT and cyber security should be continuous and integrated. But how do you make that happen? We have some ideas, but you shouldn’t think of these as discrete or linear steps. Think of them more like a series of interconnected gears: when one turns, the others do also—each part of the security plan should move in sync.
Design
Security starts with design
Design workflows that use collaborative and accountable processes across your teams to define and implement security into the IT lifecycle. If you are using technologies that have highly connected environments (like cloud), know that some of the control might be in the hands of a third-party vendor.
Some questions to discuss with your team: What kind of security controls and processes are required for your environment? How will you work with vendors? How will you communicate important security decisions between teams?
Get started:
- Define security controls and requirements
- Develop security processes collaboratively
- Keep your teams up-to-date with security standards
- Have clear methods of communicating so that when something does happen, security solutions can be implemented across the IT lifecycle as simultaneously as possible
- Choose vendors you trust and be clear what they are, and are not, responsible for
Build
Build security in using automation
DevOps uses automation to run a continuous feedback loop throughout all stages of the application life cycle. “Building security in” borrows this practice–even if you aren’t a DevOps business. Automating security checks and processes has several benefits: it prevents duplication and lessens human error, it provides a centralized dashboard for decision-making, and it makes the process of searching out and responding to threats faster. You can also use automation to build security gates, so that if a security check fails you can automatically prevent deployment.
Still, false alarms and internal threats happen. Automation needs to be managed so that it works well for the specific needs of your teams. As you build security into your infrastructure, application, and processes, ask if controls are in place to prevent unauthorized changes and access. Use encryption wherever you can.
Get started:
- Automate & integrate security testing into your build and deployment processes
- Use security gates to trigger appropriate action, whether it is to deploy or prevent deployment
- Use cryptographic algorithms and interfaces
- Choose infrastructure that has logging and monitoring capabilities
Run
Run on security enhanced platforms
Traditional models of security that rely on manual processes aren’t compatible with the security needs of new, distributed technologies like cloud. These technologies and the tools and processes that support them rely heavily on automation. Whether you are using physical, virtual, private or public cloud, make sure your infrastructure is embedded with protective and security-enhanced platforms that are common across all your environments.
Get started:
- Automate & integrate security testing into your build and deployment processes
- Infrastructure platforms should be integrated, usable, and consistent across architectures and amenable to a wide variety of processes
Manage
Manage configuration, users, and access
Don’t forget to invest in management tools that handle the automation of security configuration changes, audits, and remediations. Assigning roles early and according to your specific security needs will help you maintain a resilient security environment. Ensure privileges are assigned only to those who need them to do their work. You probably do this when people join your company, but make sure to update user data periodically and then again if they leave.
Some considerations to keep in mind: do you have tools in place to analyze and mitigate an incident? How will you use automation to automatically apply, audit, and remediate security and regulatory compliance policies across workloads?
Get started:
- Maintain an up-to-date catalog of assets and monitor access and usage
- Deploy a management solution for continuous proactive security that covers all of your infrastructure: physical, virtual, private and public cloud
- Actively manage users and access with a dashboard that allows you to keep track of all parts of the IT lifecycle
- Define security profiles with your required security controls
- Automate compliance to those security profiles
- Make sure to have both infrastructure and security as code (this helps you have a repeatable, sharable, and verifiable infrastructure and helps make compliance audits easier)
Adapt
Adapt with the changing landscape
The security landscape changes fast. Plan to revise regularly in accordance with parallel changes in governance and audit requirements. Know where to go for security warnings and advice, and use that information to adapt accordingly. Still, even with the best security plans, new attack vectors are uncovered regularly. Deploying a rapid response to a security threat is one of the most important things you can do to protect your business. Having a partner to guide you through patches, fixes, and recovery is critical to getting your business back on track.
Get started:
- Use analytics and automation to adapt: revise, update, remediate as the landscape changes
- As roles and responsibilities change, update access settings
- Keep up with governance and audit requirements
- Revise and update your policies & governance as the landscape changes
We can help
Need more guidance, or the right tools to get you on your way? Here are just a few of the resources Red Hat offers to help you fortify your enterprise.
Security resources
Developers
Red Hat Developer Program
Learn about secure programming with the Red Hat Developer Program.
Training
Red Hat Security: Linux in Physical, Virtual, and Cloud (RH415)
Manage security risk and help meet compliance requirements with our security technologies.
Support
Technical account management
Partner with a technical advisor who offers risk assessments and supportability checks.